LeSS (Large-scale Scrum), like regular Scrum, is a framework for development in which the details need to be filled in by the teams and evolved iteration by iteration, team by team. It reflects the lean thinking pillar of continuous improvement. It is a collection of suggestions for inspecting and adapting the product and process when there are many teams – at least two teams and up to groups of 500 or 1000 people.
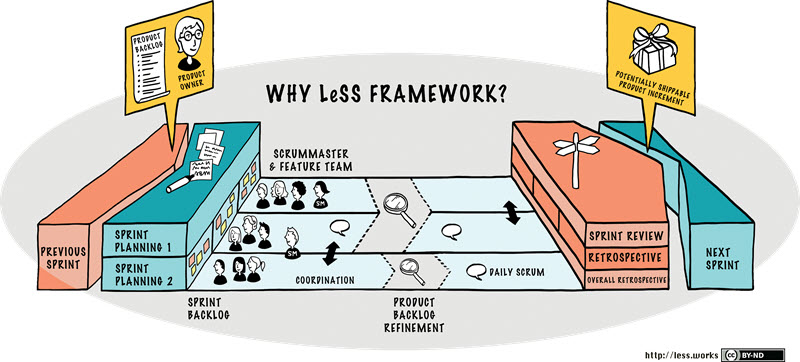
LeSS Framework is not “new and improved Scrum.” Rather, it is regular Scrum, an empirical process framework in which you can inspect and adapt to any method and work in a group of any size. Large-scale Scrum is a set of additional rules and the set of tips that we have seen work in large multi-team, multisite, and offshore agile development initiatives. These tips are experiments to try in the context of the classic Scrum framework.
LeSS framework keeps it very simple and that’s why the LeSS framework is often be mentioned with the slogan: “LeSS is more with LeSS”. The idea is that LeSS defines a “barely sufficient methodology” (a key idea in the early agile days) for a group to scale, to enable shipping every Sprint, and to enable transparency and empirical process control.
Rather than pushing a large and complex set of processes, structures, roles, and artifacts on to a group, there are more learning and adaption, less following and conformance. More value, less bureaucracy, and so on. The team should scale up a simple framework from simple elements, rather than attempt to “tailor down” a complex process framework and the Philosophy of LeSS Framework is listed as follows:

LeSS provides two different large-scale Scrum frameworks. Most of the scaling elements of LeSS are focused on directing the attention of all of the teams onto the whole product instead of “my part.” Global and “end-to-end” focus are perhaps the dominant problems to solve in scaling. The two frameworks – which are single-team Scrum scaled up – are:
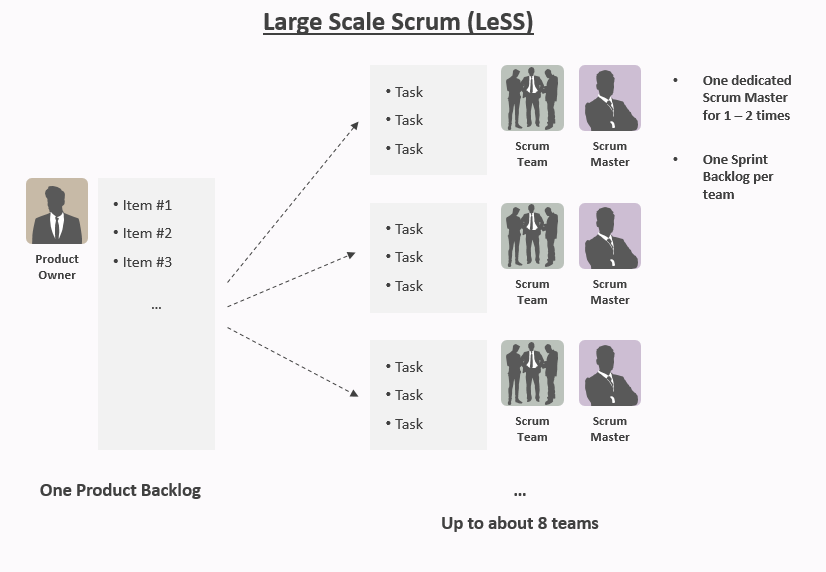
LeSS Basic -Up to eight teams with eight people each
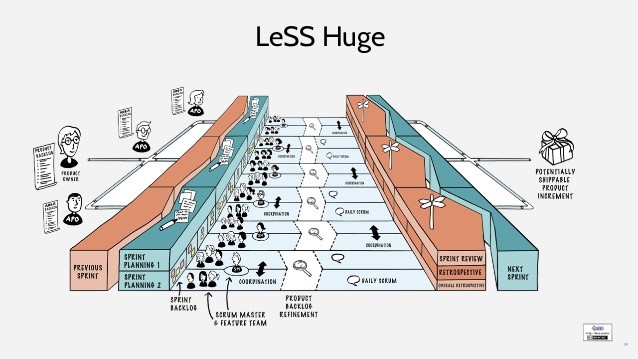
LeSS Huge – Up to a few thousand people on one product
You can organize multiple Scrum teams in many different ways, such as LeSS, Nexus, SAFe, DAD and Scrum@Scale based on our work with these frameworks which share some common patterns: Scrum at team level, many teams sharing a backlog, planning is done collaboratively across teams and the general principles of pull and self-organization. If you know Scrum well, LeSS Framework is the “no-brainer” framework for scaling the teams for your organization.