How to Draw ONE Class Diagram for Java, C# and VB?
Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a generic modeling language that is independent of any particular programming language. Generally speaking, developers should be able to read and understand the diagrams without problem, regardless of the programming language he use. But to make things easier to understand, you can optionally present your UML class model in specific language. To be specific, data types to use an attributes and operations can be presented in language specific names like 'boolean' in Java and 'bool' in C#.
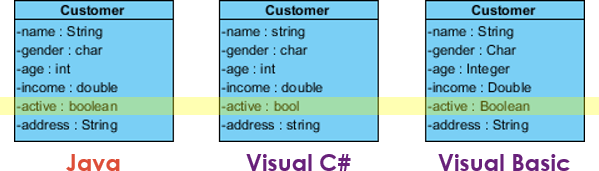
In this tutorial, we will show you how to present a class model in different programming languages.
Creating a Project in a Specific Language
In this section, we will show you how to create a new project in a specific programming language. By doing so, you can easily select language-specific types when constructing a class model. Do not worry if you have not been doing this in your production projects. You can switch between languages any time you want, which we will show you how to do in the next section.
- Select Project > New from the application toolbar.
- In the New Project window, enter Tutorial as the Name.
- By default, UML is selected as the Data type set, meaning that you can use primitive UML data types when constructing your model. Let's say we are going to draw a class diagram for a Java project. Select Java as the Data type set.

- Click Create Blank Project.
Creating a Simple UML Class Diagram
In this section, you will create a class diagram with one class and several attributes. You will be creating the attributes with primitive Java data types.
- First, create a UML class diagram. You can create a class diagram by selecting Diagram > New from the application toolbar. Select Class Diagram in the New Diagram window and then click Next. Click OK again to create the diagram.

- Create a class named User.

- Let's add an attribute named `name` to the class. Right-click on the class and select Add > Attribute from the popup menu.

- The `name` attribute is a (Java) String. You can type `name : String` to create such an attribute, but let's try something different this time. Type `name` and then click on the diagram background to create a typeless attribute.

- Right-click on the attribute and select Open Specification... from the popup menu.
- Click the dropdown menu next to the Type field. You can see a list of primitive Java data types available for selection. Now, select String and click OK to confirm.

- Now, create two more attributes: age : int and active : boolean. To save time, you can type the name and data type inline without going through the specification window.

Presenting a Class Model in Another Programming Language
Now you have a class diagram with Java data types used as attribute types. To make the diagram more C#-friendly, you can present the data types in C#.
- Select Window > Configuration > Configure Programming Language from the application toolbar.
- The Programming Language window shows the currently selected language, its supported data types, and their corresponding display names, which we will describe in more detail in a minute. Now, change the Language from Java to C#.

The list of data types is updated and is now longer than before. If you scroll, you can see some C# types like `uint` and `ulong`, which are not available in Java. So how do you read the two columns? Let's check the row for the String type. The first and second columns show 'String' and 'string', respectively. This means that the original 'String' type (available under Java) will be displayed as 'string' when the language is changed to C#.
- Click OK to confirm the change of programming language. You can now see that the `name` attribute is shown as a C# `string`, while the `active` attribute is now a C# `bool` instead of a Java `boolean`.
