Business Logic Discovery with Decision Table
Business logic reflects the business practices that set a business apart from its competitors. Understanding the business logic is critical in determining how a company can become more competitive. Unfortunately, it is not that easy.
Decision tables are tools that provide a systematic approach to mining and uncovering business logic. In a decision table, business logic is partitioned into conditions, actions, and rules.
Case Study - Supermarket Delivery Service
V&P is the largest supermarket chain in the city. As the city's foremost supermarket, V&P is dedicated to providing its customers with quality products and services. Recently, V&P has decided to review its delivery service to achieve the following:
- Standardize the services of all branches to provide customers with a unified shopping experience.
- Review and possibly refine the current service to make it more attractive.
To achieve these goals, the chief operating officer of V&P held a meeting with the store managers to review and discuss the current delivery policy. Here are the notes drafted during the meeting:
- Orders of $80 and above, with a weight lower than 10 kg, will be delivered for free.
- Delivery service is not available if the order value is less than $80.
- Regardless of the amount purchased, delivery service is not available when the destination is in an outlying island.
Some managers believe there are more rules than the three listed above. Unfortunately, they are unable to figure them out, especially since the rules were never documented anywhere. One of the managers suggests doing a bit of analysis by porting the rules into a decision table. Here is the decision table he drew by transforming the three known rules into table form:

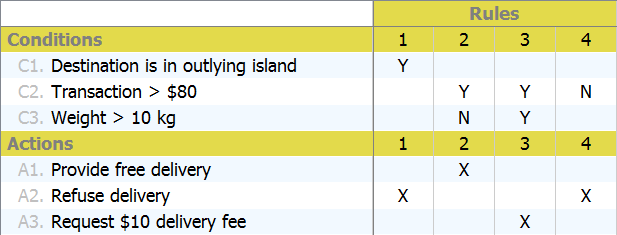
By checking the decision table, one of the managers said, "What about heavier than 10 kg? As I remember, orders weighing heavier than 10 kg will incur a $10 delivery fee." The managers were enlightened. They then revised the decision table by adding this new rule. Here is the updated table:
Try it Out
- Download the decision table sample project.
- Start Visual Paradigm and open the downloaded project file.
- Open the decision table.

- Based on the case study above, we have to add this rule to the table: "Orders weighing heavier than 10kg will incur a $10 delivery fee." The new rule involves a new business decision—to request a $10 delivery fee. So let's add a new action first. Move the mouse pointer over the compartment caption Actions. Click on the add button near the caption.

- Enter Request $10 delivery fee as the action.
- We can now add the rule to the decision table. Similar to adding an action, add a rule by clicking the add button near the compartment caption Rules.

- Let's express the rule by properly filling in the conditions and actions cells. Under the new rule, double-click on the cell for condition Transaction > $80. Select Y in the drop-down menu.

- Similarly, put Y for the condition Weight > 10 kg.

- The decision of this rule is to request a $10 delivery fee. Mark the action Request $10 delivery fee with X.

-
Let's place the rule next to the second rule so that readers can understand the different business decisions to make when the order is more or less than 10 KG. Right-click on the fourth rule and select Move Left from the popup menu.

Finally, the decision table should look like this:
Conclusion
Based on a decision table, you can easily discover hidden rules by evaluating different combinations of conditions.
A decision table also helps in generating new ideas related to decision-making. Continuing with the supermarket example, the managers may come up with a new rule like: "Request an additional payment when the packed goods are too big in size."
The more thoughtful the decision-making, the better the business.